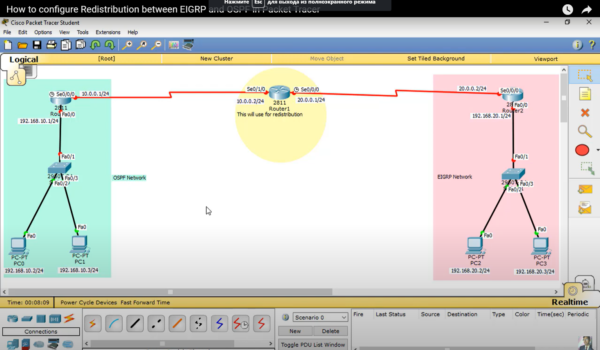
Route redistribution between OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a fundamental aspect of network management and optimization. It allows networks that use different routing protocols to exchange routing information effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of route redistribution, discussing its significance, best practices, and potential challenges.
Understanding Route Redistribution
Route redistribution is the process of transferring routing information from one routing domain to another. In our context, we’ll explore how OSPF and EIGRP can coexist and share route information.
The Role of Routing Protocols
Routing protocols are the backbone of network communication. OSPF and EIGRP are two prominent routing protocols:
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
- Developed for IP networks;
- Uses a link-state routing algorithm;
- Preferred for large and complex networks;
- Hierarchical structure with areas.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
- Proprietary Cisco protocol;
- Employs a hybrid routing algorithm;
- Ideal for smaller, less complex networks;
- Rapid convergence and efficient bandwidth usage.
Why Route Redistribution Matters
Route redistribution is crucial for several reasons:
- Network Expansion: When organizations merge or expand, they often have networks running different routing protocols. Redistribution facilitates seamless integration;
- Protocol Migration: Companies may decide to switch from OSPF to EIGRP or vice versa. Redistribution ensures a smooth transition;
- Optimizing Traffic Flow: Different routing protocols may be better suited for specific network segments. Redistribution allows for route optimization.
Challenges in Route Redistribution
Route redistribution is not without its challenges:
- Routing Metric Mismatch: OSPF and EIGRP use different metrics to determine the best path. Converting these metrics can be complex;
- Route Selection: When routes from multiple sources are available, the router must select the best route, considering metrics, administrative distance, and routing protocol preferences;
- Loop Prevention: Careful filtering is essential to prevent routing loops, which can disrupt the entire network.
Best Practices for Route Redistribution
Successful route redistribution requires careful planning and adherence to best practices:
1. Clear Route Filtering
Implement precise route filtering to control which routes are redistributed. This minimizes the risk of routing loops and ensures only relevant routes are shared.
2. Metric Conversion
When redistributing routes between OSPF and EIGRP, convert metrics appropriately. This ensures that routing decisions are made based on a unified metric.
3. Administrative Distance
Understand the administrative distance of each routing protocol. Routes with lower administrative distances take precedence.
4. Route Tagging
Use route tags to mark redistributed routes. This helps in route identification and troubleshooting.
5. Monitoring and Testing
Regularly monitor the redistributed routes and conduct testing to identify and address any issues promptly.
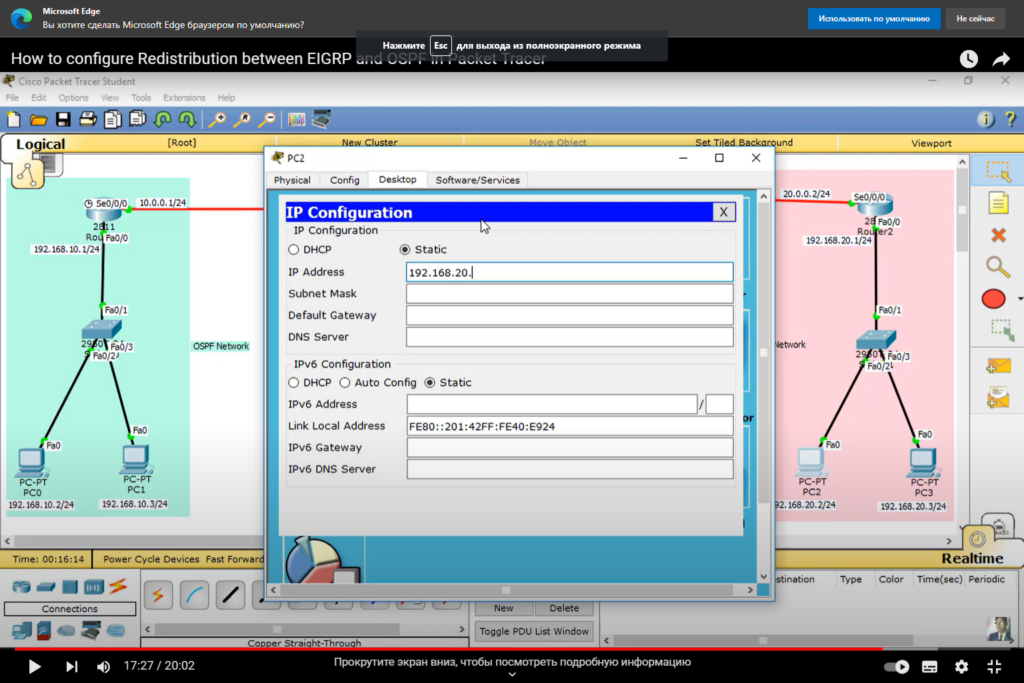
Route Redistribution in Action
Let’s illustrate route redistribution with a practical example:
Suppose we have two branch offices, one using OSPF and the other EIGRP. We want them to exchange routes seamlessly.
Configuration Steps
- Identify the routes to be redistributed;
- Apply route filters to select specific routes;
- Convert metrics to ensure compatibility;
- Verify the configuration using show commands.
By following these steps and considering best practices, you can achieve effective route redistribution.
Route Redistribution: OSPF to EIGRP vs. EIGRP to OSPF
When redistributing routes, the direction matters. Let’s explore the key differences:
OSPF to EIGRP
- OSPF routes are injected into the EIGRP domain;
- Conversion of metrics and administrative distance is necessary;
- EIGRP routers may need route summarization to prevent excessive route entries.
EIGRP to OSPF
- EIGRP routes are injected into the OSPF domain;
- Metric conversion is essential to align with OSPF’s link-state algorithm;
- OSPF areas play a significant role in managing redistributed routes.
Comparing OSPF and EIGRP
Before we conclude, let’s compare OSPF and EIGRP to understand their strengths and weaknesses:
| Aspect | OSPF | EIGRP |
|---|---|---|
| Routing Algorithm | Link-state routing | Hybrid routing |
| Network Size | Suitable for large networks | Ideal for small to medium networks |
| Convergence Speed | Slower convergence | Rapid convergence |
| Configuration | Complex configuration | Simpler configuration |
| Administrative | Based on cost | Based on bandwidth and delay |
Conclusion
Route redistribution between OSPF and EIGRP is a crucial skill for network administrators and engineers. It enables networks to function cohesively, even when using different routing protocols. By following best practices, understanding the nuances, and considering the direction of redistribution, you can optimize your network’s performance and reliability.
FAQs
Route redistribution enables different routing protocols to exchange routing information within a network. It is vital for network integration and optimization.
To prevent routing loops, use precise route filtering, and carefully configure administrative distances and metric conversions.
The choice between OSPF and EIGRP depends on the network size and complexity. OSPF is suitable for large networks, while EIGRP is ideal for smaller ones.
OSPF to EIGRP redistribution involves metric conversion and potential route summarization. EIGRP to OSPF requires metric alignment and consideration of OSPF areas.
Route tagging helps identify redistributed routes and aids in troubleshooting and monitoring network traffic.